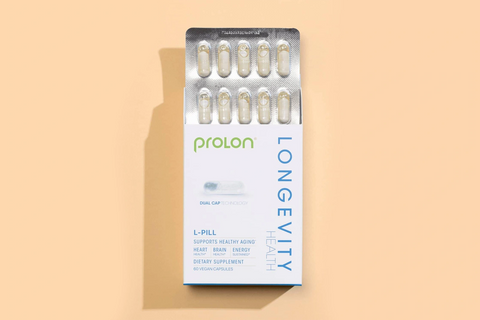


o 3 rate da 0,00 € senza interessi con
Hai 18 anni o più?
Ci dispiace, ma il contenuto di questa sezione non è adatto ai minorenni




o 3 rate da 0,00 € senza interessi con
 L-Pill est le seul complément que je prendrais. - Dr Valter Longo
L-Pill est le seul complément que je prendrais. - Dr Valter Longo

La qualité et le rythme de notre vieillissement biologique sont les principaux déterminants d'une vie longue et saine. La force de L-Pill réside dans sa combinaison unique de quatre ingrédients naturels qui ont été étudiés pour leurs bénéfices potentiels dans le cadre d'un vieillissement en bonne santé, avec des fonctions énergisantes et antioxydantes.
DHA
est un acide gras polyinsaturé oméga-3 essentiel, qui entre dans la composition des phospholipides de divers organes, notamment le cœur, le cerveau et la rétine. L'apport en DHA contribue au maintien d'une fonction cérébrale physiologique et d'une capacité visuelle normale. Des études montrent que les populations européennes consomment peu d'aliments contenant du DHA, ce qui crée des situations de carence auxquelles il est possible de remédier par une supplémentation.
Lysine
Il s'agit d'un acide aminé essentiel pour l'homme, qui doit donc être apporté par l'alimentation. La lysine joue plusieurs rôles chez l'homme, principalement dans la protéinogénèse, mais aussi dans la réticulation des polypeptides du collagène.
Extrait de Wasabi Japonica riche en isothiocyanates
Les isothiocyanates proviennent de l'hydrolyse des glucosinolates, des composés soufrés à l'odeur caractéristique, présents dans les légumes crucifères, bien connus pour leur fonction digestive.
Extrait de sucre de canne riche en polyphénols et en flavonoïdes
Les polyphénols constituent un large groupe de substances organiques naturelles dont les flavonoïdes. De nombreuses études ont établi un lien entre la consommation de flavonoïdes, l'action anti-âge et la capacité à éliminer les radicaux libres par des processus de transfert d'électrons.
Extrait de thé vert (catéchines, caféine)
L'extrait de feuille de Camellia sinensis, conformément aux directives du ministère de la santé, contribue au drainage des fluides corporels, à l'équilibre du poids corporel, à la fonction intestinale normale, au tonus et à l'antioxydation.
POURQUOI L-PILL
L'innovation rencontre la nature.
Notre L-PILL garantit un dosage optimal de ces ingrédients de manière sûre et efficace. Le DHA est lié à l'acide aminé essentiel L-lysine pour former un sel, ce qui rend le DHA plus facilement assimilable par l'organisme, augmentant ainsi son efficacité
COMMENT ÇA MARCHE
Comment et quand l'utiliser L-Pill ?
Prendre deux gélules par jour avant les repas. Il peut être utilisé quotidiennement par toute personne âgée de 18 à 80 ans. Vous pouvez arrêter et recommencer à tout moment, à votre convenance. Si vous avez des problèmes de santé, consultez votre médecin avant de les prendre. Ne prenez pas L-Pill si vous êtes allergique à l’un de ses ingrédients.
Afin de maximiser les bénéfices de L-Pill, il est recommandé de prendre après : ProLon Fasting Mimicking Diet, ProLon Reset, ou des périodes de jeûne intermittent avec la Nutrition Bar ou le Fasting Shake pour maintenir les bénéfices obtenus au niveau du microbiote intestinal et statut antioxydant.
Avec L-Pill de ProLon, vous ne choisissez pas seulement un complément, mais un partenaire dans votre voyage vers la longévité et un vieillissement en bonne santé. Alors que nous cherchons continuellement à progresser dans la compréhension de la longévité, nous nous engageons à vous offrir le meilleur de ce que la science et la nature offrent aujourd'hui.
Références sélectionnées
Huile d'algues DHA
Wasabi Japonica
Med._2012
Flavonoïdes et polyphénols de l'extrait de sucre de canne
Catéchines et caféine de l'extrait de thé vert

